HAIR TRANSPLANTATION
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a modern and effective hair transplant procedure that has revolutionized the field of hair restoration. This technique is widely recognized as the go-to treatment for patients suffering from androgenetic alopecia, more commonly known as male or female pattern baldness.
The Basics
FUE is a method of harvesting or "extracting" donor hair, a key phase of all hair transplant procedures. In this process, individual follicular units (natural groupings of one to four hairs) are extracted directly from the patient's donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp, and then transplanted into the thinning or balding areas.
The Procedure
The FUE hair transplant process is an intricate one, requiring precision and expertise. It begins with the administration of local anesthesia to numb the donor area. Then, the surgeon uses a specialized instrument to make a small circular incision around the follicular unit, separating it from the surrounding tissue. The unit is then extracted directly from the scalp, leaving a small open hole.
The process is repeated until the surgeon has harvested enough follicular units for the planned hair transplant. The small open holes left from the extraction are left to heal over the next several days, resulting in tiny white scars scattered throughout the donor area.
The extracted follicular units are then prepared for transplantation. Meanwhile, the recipient area is numbed with local anesthesia. The surgeon makes tiny recipient sites in the balding areas using a fine needle-point instrument. The follicular units are then placed into these sites, where they will grow into healthy hair-producing follicles.
Before and immediately after 1000 grafts.
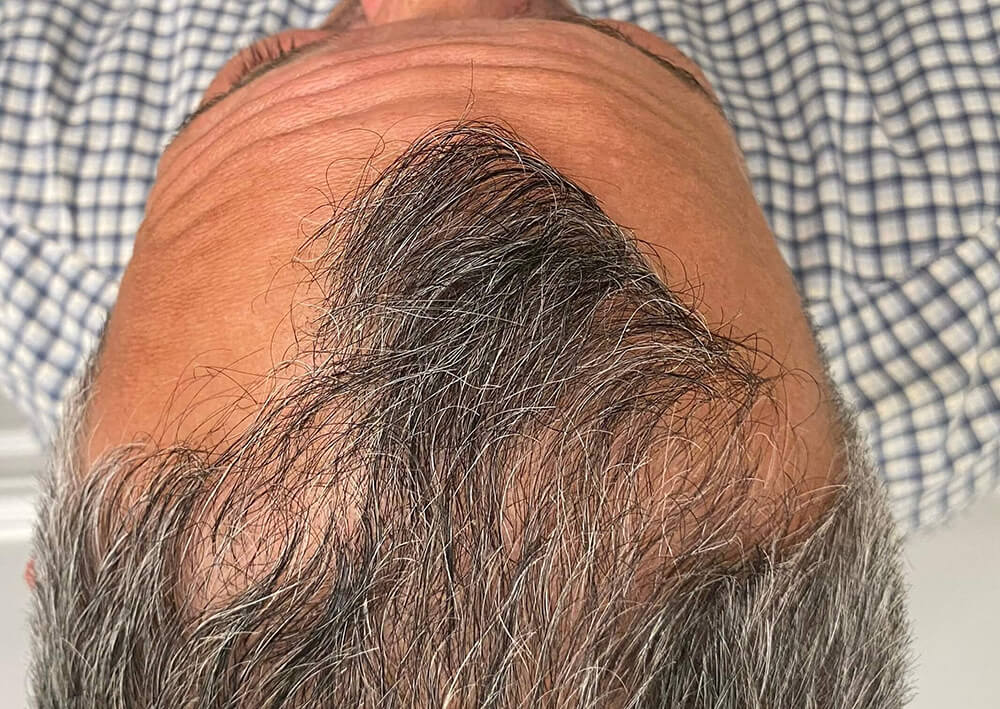 | 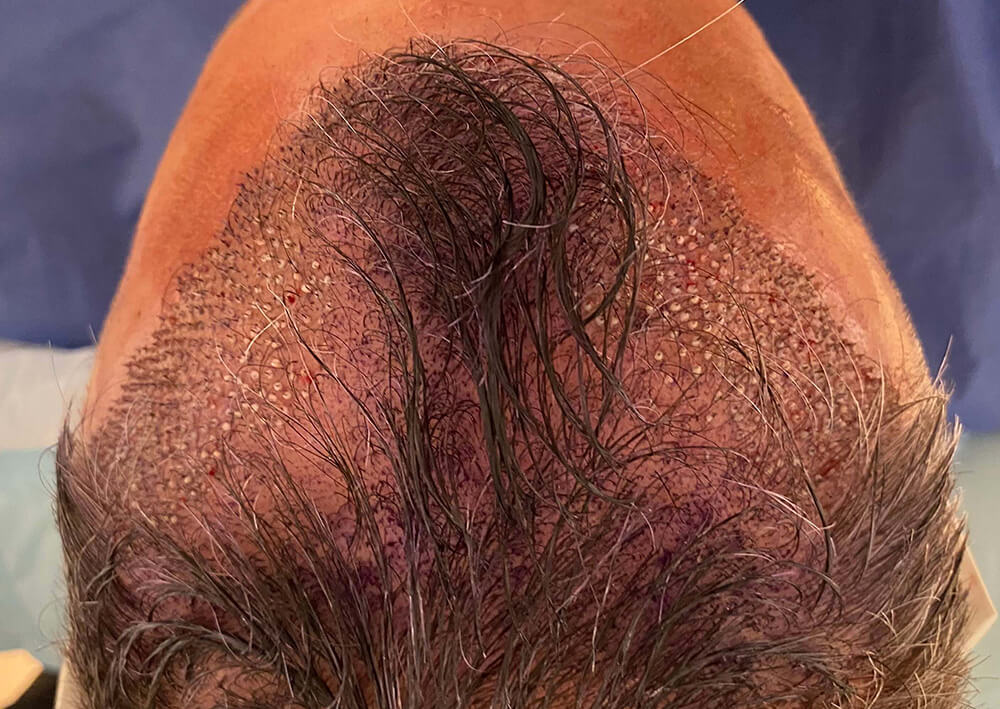 |
Advantages
There are several advantages of FUE over the older strip harvesting method, also known as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). Firstly, FUE avoids the linear scar left by strip harvesting, which is particularly beneficial for patients who wish to wear their hair short. The tiny dot scars of FUE are practically invisible and spread over a large area in the back of the head.
FUE is also less invasive than the strip method. As it doesn't involve the removal of a strip of scalp, sutures aren't necessary. This generally results in a more comfortable post-operative experience and a faster recovery time.
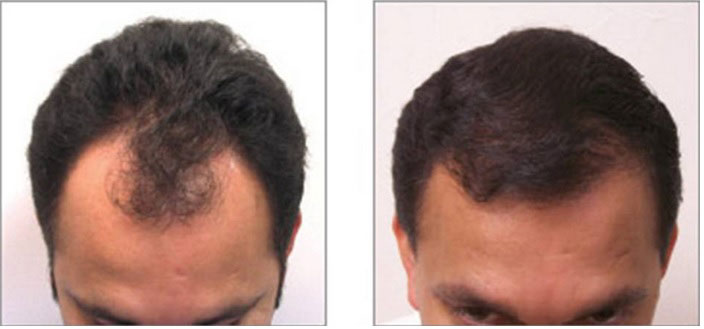
Drawbacks
Despite its benefits, FUE is not without drawbacks. The main downside is the potential overharvesting of the donor area. As FUE requires a larger area compared to FUT, there's a higher risk of thinning the donor area excessively.
FUE procedures also tend to be more time-consuming due to the meticulous nature of harvesting individual follicular units. This often makes the process more expensive.
Potential Outcomes
The outcomes of FUE hair transplants can vary based on the skill of the implanter, the characteristics of the patient's hair, and post-operative care. Most patients can expect to see new hair growth around three to four months after the procedure, with full growth evident after a year.
FUE transplants have a high success rate, and most patients report high satisfaction levels. However, like all medical procedures, it carries a degree of risk, and not all transplants will be successful. Patients should also bear in mind that hair loss can continue in non-transplanted areas, which may require additional procedures down the line.
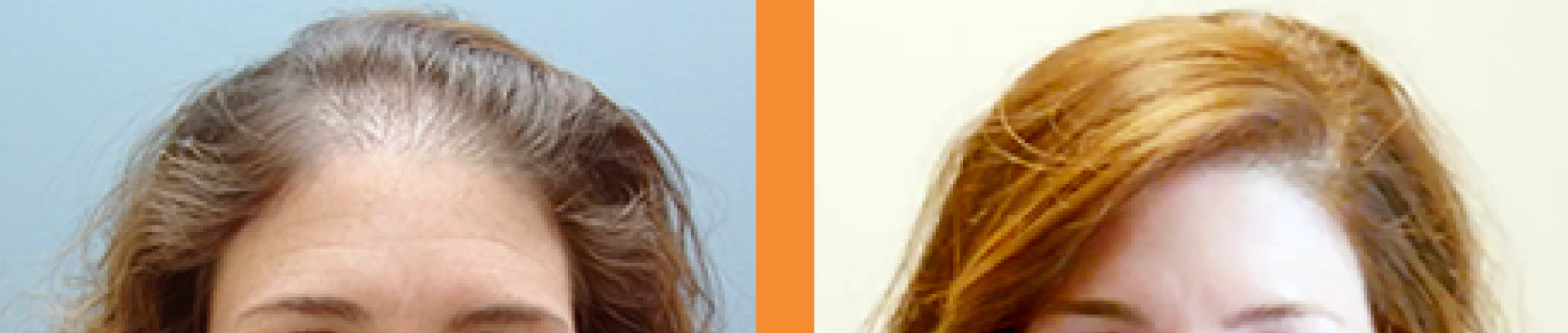

Aftercare
Post-operative care is crucial for the success of a hair transplant. Patients should avoid strenuous activity and direct sun exposure for at least a few weeks post-operation. The transplanted hair will typically fall out after a few weeks – this is entirely normal and part of the process. The follicles then start producing new hair.
FUE hair transplantation is a popular, minimally invasive, and highly effective method for treating pattern baldness. While the procedure does carry some drawbacks and risks, the potential for significant improvement in hair coverage and the high satisfaction rates make it a highly appealing option for those battling with hair loss. As always, it is crucial to consult with an experienced hair transplant surgeon to understand which procedure is the best fit for your specific needs and circumstances.
Hair Transplantation for Gender Dysphoria
Hair transplantation can be a significant component in the process of transitioning for many transgender individuals. For transgender women (male-to-female transitions), male pattern baldness or a naturally high hairline can hinder the desired feminine appearance. For transgender men (female-to-male transitions), transplantation can be used to create facial hair that's typically associated with a more masculine appearance. Let's delve into the specifics of both scenarios.
Hair Transplants for Transgender Women
For many transgender women, hair plays a significant role in shaping their identity and femininity. Male pattern baldness, a receding hairline, or a naturally high forehead can create significant dysphoria. Hair transplantation can be a viable solution in these cases, providing a permanent, natural-looking result. Hair transplantation can often be performed after hairline advancement surgery creating an optimal outcome.
The process is similar to traditional hair transplant procedures. For transgender women, the surgeon might lower the hairline and round out the corners to create a more traditionally feminine hairline. It's essential to note that hormone replacement therapy (HRT), commonly used during transition, often results in some natural hair regrowth. Therefore, surgeons may suggest waiting until the full effects of HRT are visible before proceeding with a hair transplant.
The techniques used for hair transplant in transgender women are the same as those for cisgender men: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). The choice between these two methods will depend on the individual's hair characteristics, the size of the area to be covered, and personal preference.
Hair Transplants for Transgender Men
For transgender men, the lack of a beard or other facial hair can be a source of distress. Here, hair transplantation can play a pivotal role. Donor hair, typically from the back of the head, is transplanted into the desired facial areas, most commonly the chin, upper lip, and cheeks. Over time, this hair grows just like natural facial hair and can be shaved or styled in any preferred manner.
The transplant procedure for facial hair usually employs the FUE method due to its precision and the fact it leaves minimal scarring. Post-procedure care is critical and requires careful cleaning of the transplant area. It's worth mentioning that hormone therapy in transgender men often stimulates some facial hair growth. Like with transgender women, doctors may advise patients to wait until hormone therapy has taken full effect before deciding on a transplant.
Hair transplantation can significantly contribute to gender transition, helping transgender individuals align their physical appearance with their gender identity. As with any medical procedure, potential patients should have thorough consultations with experienced medical professionals. This ensures they are well-informed about the procedure's benefits, risks, and expected results. It's crucial that the chosen surgeon understands the specific needs and goals of transgender patients, and can deliver results that enhance their transition process.
What is NeoGraft?
 Neograft is a device designed to automate the collection and placement of individual hair follicles in the FUE procedure. The Neograft system uses pneumatic pressure (air pressure) to extract follicular units from the donor area and then implant them into the recipient area. It eliminates the need for a surgeon to manually extract and implant each unit, thus reducing the time and labor involved in a traditional FUE procedure.
Neograft is a device designed to automate the collection and placement of individual hair follicles in the FUE procedure. The Neograft system uses pneumatic pressure (air pressure) to extract follicular units from the donor area and then implant them into the recipient area. It eliminates the need for a surgeon to manually extract and implant each unit, thus reducing the time and labor involved in a traditional FUE procedure.Benefits of NeoGraft
- Less Invasive: The Neograft system eliminates the need for a scalpel, stitches, and staples, which are often required in traditional strip method or Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). This results in less discomfort and a quicker recovery period for the patient.
- No Linear Scarring: One of the most significant advantages of Neograft (and FUE in general) is that it leaves no linear scar, making it an excellent option for patients who wish to wear their hair short.
- Greater Precision: The Neograft device allows for precise extraction and placement of hair follicles, which can lead to more natural-looking results.
- Efficiency: The automated system can handle a larger number of grafts at one time compared to manual FUE. This makes it possible to treat more extensive areas of baldness in fewer sessions.
Limitations of NeoGraft
- Operator Dependent: Despite its technological advancements, the outcome of a Neograft procedure is highly dependent on the skill and experience of the operator. A well-trained and experienced professional is vital for a successful transplant.
- Cost: Neograft procedures can be more expensive than traditional FUE due to the cost of the technology.
- Availability: Not all clinics offer Neograft as an option, as it requires specific training and a substantial investment in equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Neograft represents a significant advancement in hair transplantation technology. Its less invasive nature, precision, and efficiency make it a highly appealing option for many individuals seeking hair restoration. However, like any medical procedure, it's crucial for potential patients to research and consult with experienced professionals to understand if this method is suitable for their specific situation. Despite the technology used, the skill, experience, and artistry of the surgeon remain the most critical factors in achieving the desired results in hair transplantation.